Saturday, 21 December 2019
Saturday, 14 December 2019
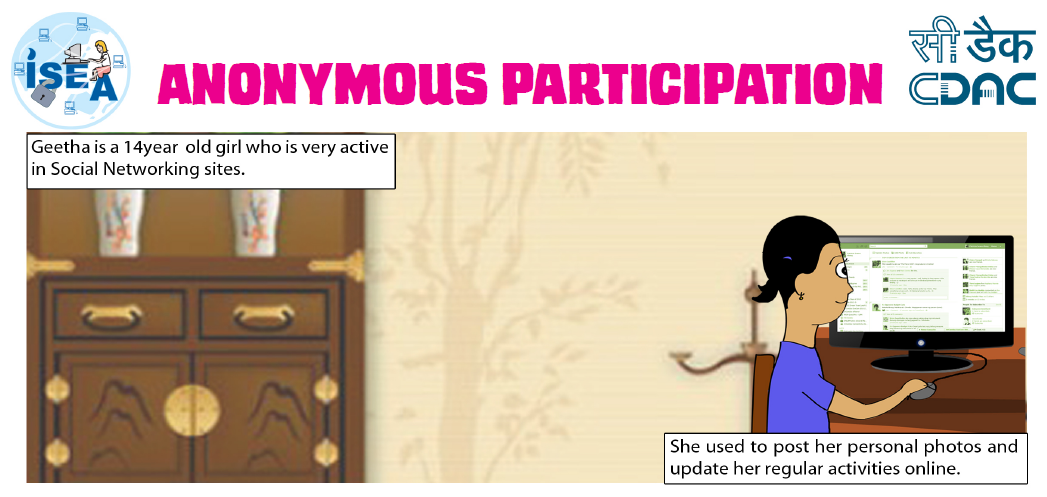
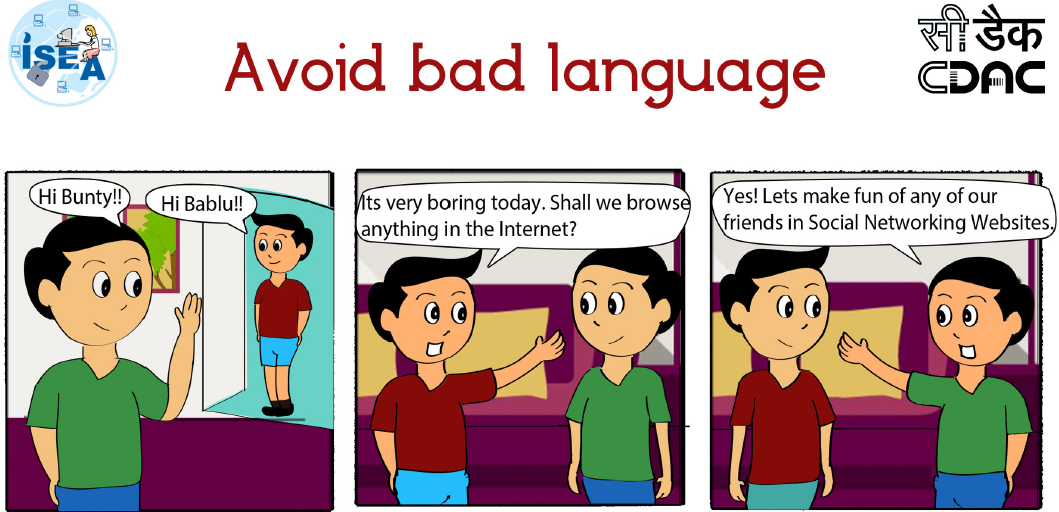
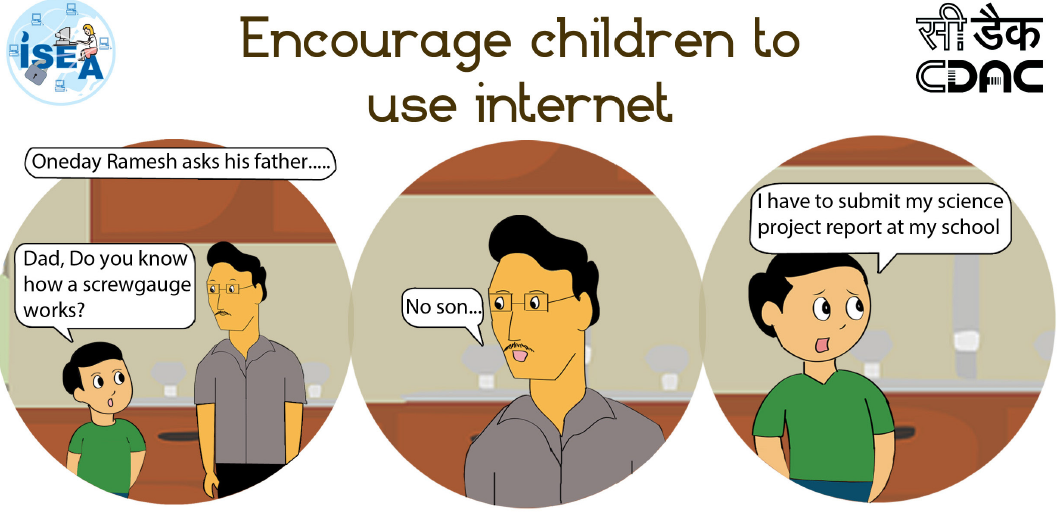
ISEA Cyber Safety Cartoon Stories - Must Read for Kids to Learn about Cyber Safety
Friday, 13 December 2019
Cyber Threats - Self Assessment
Thursday, 12 December 2019
Tuesday, 10 December 2019
Cyber Threats to Children
According to statistics released by the National Crime Record Bureau (NCRB) on October 22, 2019 Cybercrimes in India almost doubled in 2017. Karnataka had the highest rate of cybercrime with Bengaluru registering the most number of cybercrime cases in 2018 , followed by Assam, Telangana, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh. India ranked third in the list of countries where the highest number of cyber threats were detected, and second in terms of targeted attacks in 2017, according to security software firm Symantec.
Let’s see what are some of the online threats that we should be aware of.
Malicious Content
One of the issues that we should be careful about is the Malicious Contents.
• Malicious content means documents or programs infected with viruses, or websites that try to infect your computer with virus. The infected site will cause your computer to be infected and these virus may steal your personal information, delete your files, or encrypt the data on the victims computer, then asking for payment to get the data. Hope you might have heard about the Wannacry ranswomware attach in 2017.
• Most often browsers like Google Chrome or Firefox prevents you from accessing such infected websites displaying a warning message. Whenever you see such warnings from the browser, do not proceed to visit the website.
Obscene Content
Similar is the case of Obscene Content online. There are a good number of shock sites on the internet. Shock sites mean the sites that have content with high shock value material that includes pornography, violence, racist, hatred, profane, vulguar and other provocative materials.
•There may be visual with images and videos or verbal with profane languages or hate speeches. Videos of violence, murder, suicide and the like are being shared widely on social media now days. Unfortunately, our society, including the adults, seems to enjoy such violent content. If you receive such videos or files just delete them. Never watch them or forward them. Such content may have severe psychological and emotional impact on the viewers.
Also think about the violation of the rights of the victim or the victim’s family. How it will affect them when the photographs/videos of the violent deaths/accidents of their beloved one are being circulated over the Internet, reminding them of the tragic incident.
Malware
• Malware is computer software that is installed without the knowledge of permission of the victim and performs harmful actions on the computer. These software may personal information from the computer and send it to the attacker. Your computer may get infected when you download email attachments or try to install freeware software that you download from the internet.
• The infected computer may be used a ‘botnet’ to perform attacks on other computers or to mine cryptocurrency. A botnet is a number of Internet-connected devices, each of which is running one or more bots.Botnets can be used to perform Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, steal data, send spam, and allows the attacker to access the device and its connection.
Online Scams
Another common threat that people fall prey to are online Scams.
• Have you got an email from a Nigerial prince or an African accountant ready to share their fortune (worth millions) with you?
• Or an email offering scholarship to study abroad? Such techquiques are adopted by the fraudulent people to get important personal information and to extract money form the victims in the form of service charges or advance for getting the scholarship or lottery amount.
• Always remember, if an offer sounds too good to be true, it probably isn't true
• Don’t believe in offers that offer too much
It is quite unfortunate that even the educated people fall prey to such scams. If you go through the newspapers, you will find many stories of such scams.
Online Predators or Cyber Groomers.
Another serious issue, as far as childrens are concerned, is the presence of Online Predators or Cyber Groomers.
• An online predator is someone who sexually exploits a child over the Internet. Online predators normally hide their identity and pretend to be someone that the child may think safe.
• In cyber grooming, the online predators befriend the children through social media and builds an emotional bond. These predators need not be strangers. Even known people, including relatives and family friends may try to exploit a child. They try to attract children into sexual conversations and also persuade to meet personally. They may also send obscene content to the child and ask children to send pictures of themselves
• Chat rooms, instant messaging, Internet forums, social networking sites, mobile phones, and video game consoles have issues with online predations. If you ever come in contact such people, always report such cases to your parent or teacher immediately.
• Keep in mind that people are not always who they say they are.
Cyber Bullying
Cyber Bullying is another serious online threat. India ranks at number 3 in the list of online bullying cases as per the survey conducted by Microsoft in 2012 in 25 countries Cyber bullying is the bullying that takes place on digital devices or through digital media
We will be having a separate discussion on cyber bullying where we will discuss this in detail
Digital Privacy & Identity Theft
Now let’s take a look at Digital Privacy & Identity Theft
Are you wondering how a student will be affected by identity theft? Personal information is a hot commodity that has huge demand and can be monetized. You can have a look at the news report regarding the case where the data of hundreds of thousands of applicants who took the National Eligibility and Entrance Test (NEET) in 2018 are made available online for sale. If you find it unbelievable you can see an email we have received which offers personal information of various categories of students for sale. How do they get these information? Be careful when you filling online forms or registering on various websites that offers to provide CBSE question papers, scholarship information and other materials. There may legitimate and free website that may offer similar materials without asking your personal information. Avoid the website which ask you to provide your personal information to access content. If you have to provide such information, make sure to read their privacy policy.
• What are the information we should not provide?
• Never provide your personal information like your school admission number, mobile number, parental details, aadhar number etc. online
• Also Do not post any compromising photographs online – remember what we have learned in the Digital Footprint session regarding the images posted. Even if you delete it later, it may be available some where on the internet
• Don’t fall prey to online lucky draws, fake offers and fake tests that ask you to provide personal information to register
• Try to avoid Public Wi-Fi and only Use Legitimate networks to access internet.
• It is also advisable to Disable auto-connect feature of the laptop and smart phones.
• Turn on firewall on your computer and install antivirus. Update your operating system and antivirus regularly.
• Don’t forget to Logout after use on public systems
Techniques to Steal Personal Information
Now, let’s see various techniques to steal personal information. Most common method is Phishing.
Phishing is an attempt to fraudulently obtain sensitive information through e-mails directing you to enter personal information on a website. The victims are contact through e-mail that seems to be from a legitimate company or business asking them to take immediate action for getting some financial benefit or to protect their information.
They may have malicious attachments and links. The attachments may install malwares on your computer. The links may lead you to phishing websites. So never click on the link, if you are suspicious. How can we identify phishing messages. One way is to look at the email address – the email may not be from a public domain like gmail or yahoo. The mailid and the display name may not be related at all. Don’t be fooled if you see the official log inside the mail, anybody can embed a logo inside the mail.
Another way to identify such mails are to look at the content. There will be grammatical errors in the mail. Also there will be some kind of urgency in the message. It will ask to respond or take action immediately
Pharming
Pharming is the technique to redirect a website's traffic to another, fake site. The attackers install malicious code on the victim’s computer. So when you are trying to visit a website or doing an online search your browser may take you a malicious website.
At a higher level this can happen on a server also where the webserver of the website you are visiting is infected.
Smishing and vishing are also techniques used to extract information.
Smishing (SMS phishing) is a type of phishing attack conducted using SMS (Short Message Services) on cell phones.
Just like email phishing scams, smishing messages typically include a threat or a temptation to click a link or call a number and hand over sensitive information. Sometimes they might suggest you install some security software, which turns out to be malware.
Vishing (voice or VoIP phishing) is another tactic in which individuals are tricked into revealing critical financial or personal information to unauthorized entities by voice email, VoIP (voice over IP), or landline or cellular telephone using fake caller ids.
These are mainly used to get credit card details and account details
Cybersquatting
Another interesting technique is Cybersquatting. Though cybersquatting targets companies or businesses, we may have a look at these techniques also to learn about the technique.
A cybersquatter is someone who registers a domain name in bad faith and intent to profit from the goodwill of a trademark belonging to someone else. How does this benefit a cyber squatter? We have learned earlier about trademarks and copyrights. If someone who is not a trademark holder registers a domain name that includes a well-known trademark, they may be cybersquatting. They do this hoping to sell the domain name to rightful owner at a later stage to make a huge profit.
An interesting case on cybersquatting is the case of Microsoft when they filed a case against a Canadian teenager by the name of Mike Rowe. What Mike did is he created his part-time web design business and registered his domain as, MikeRoweSoft.com, that sounded too similar to Microsoft.com. Microsoft offered to pay him $10 compensation to get the domain name, but Mike Rowe asked for
$10,000. Microsoft filed a case to WIPO.Because of his intent to profit from selling the domain to Microsoft, it was held to be cybersquatting and Rowe was handed a cease and desist order by the WIPO.
Typosquatting
Another method of cybersqatting is Typosquatting.
This technique employs similar urls for popular websites and depends on the typing errors of users to get traffic to their sites. This one we should be aware of as it may affect us also. A well known example is facebok.com with a single “O”.
To avoid this, bookmark the sites you use often (using the “Bookmarks” or “Favorites” function in your browser) rather than typing them in the address bar.
Combosquatting is a newer form of cybersquatting that combines a popular trademark and a string of words or phrases with the use of hyphens. Combosquatting is a technique used in many phishing email campaigns. If a customer sees the trademark of a brand they know and trust when they look at the email address of the sender, they will be inclined to follow the link.
Eg. Yahoo-security.com Let’s be Cyber Smart!
There are so many cases of cybersquatting reported in the media. Can you find out few interesting cases?
Hour of Code
 Library is organising Hour of Code events in connection with the Computer Science Education Week joining the global movement to demystify "code", to show that anybody can learn the basics, and to broaden participation in the field of computer.
Library is organising Hour of Code events in connection with the Computer Science Education Week joining the global movement to demystify "code", to show that anybody can learn the basics, and to broaden participation in the field of computer.Thursday, 21 November 2019
Digital Footprint - Self Assessment
Copyright, Trademark and Patents - Self Assessment
Monday, 18 November 2019
Mobile Security Tips
Secure your Device: Secure your mobile with a strong password or fingerprint detestion. Change any default passwords on your mobile device to ones that would be difficult for someone to guess. Use different passwords for different programs and devices. Do not choose options that allow your device to remember your passwords. Set the password lock time also very short - 30 seconds.
Keep software and the device up to date. Install updates for apps and your device’s operating system as soon as they are available. Do not ignore the friendly popups reminding you to update your mobile and the applications. Keeping the software on your mobile device up to date will prevent attackers from being able to take advantage of known vulnerabilities.
Disable remote connectivity after Use. Some mobile devices are equipped with wireless technologies, such as Bluetooth, that can connect to other devices. Disable these features when they are not in use. Turn them on when you need them and only connected to trusted networks.
Think Before you Post. Before posting photos or messages to the social media, think. Think whether it is required, is it something that reveals your personal information and whether it will harm someone
Take Care. Always keep your mobile locked. Do not leave your mobile unattended in a public place. Do not hand it over to strangers. If it is really required to hand over the phone to someone, use the second space/guest mode feature available in most smart phones.
Learn More about Your Apps. Learn more about the apps you have installed on your mobile. Read the reviews and see the permissions required before installing them. Be aware that apps may request access to your location and personal information. The permission asked by the application should be something required for its proper functioning. Also do not install third-party apps. If it is really needed, do some research before installing it.
Be Cautious about Public Wifi. We all want to save our data and will be happy to access internet through a public Wifi. If you are using it, do not use it for transmitting any sensitive information.
Take a Backup. Take a back up of your data regularly. You can use the cloud services to backup or connect to your pc to backup contact list, important photos, videos, documents and other information.
Anti-virus and Anti-malware: Having a good antivirus or antimalware can help you to prevent any damage if you happen to download some malicious content unknowingly
Copyright, Trademark and Patents
What is Copyright?
Copyright is a form of protection granted by the law of a country for original works of authorship. When anyone prepare an original work of literature, art, music or any other creative work, the person automatically own the copyright to it.The author/creator of the original work will have the exclusive rights to reproduce the work (make copies) and distribute the work, public performance of the work (drama, play, musical concert etc) and to make derivative of the work (adaptation or translation). It means, no one can do any of the things mentioned above to the copyrighted works in any form without the permission of the copyright owner.
There are some limitations and exceptions to the copyright and one such case is the "Fair Use".
Works Protected by Copyright
Copyright may apply to a wide range of creative, intellectual, or artistic forms, or "works".- Literary works (poems, theses, fiction, plays and other literary works)
- Motion pictures, choreography, musical compositions, sound recordings
- Paintings, drawings, sculptures, photographs
- Computer software
- Radio and television broadcasts, and
- Industrial and architectural designs.
What is not Protected?
Copyright will not protect the ideas or principles covered in a work. It will not protect names of products, titles, business names, slogans, formulas etc. Works that are not in a tangible form (written, audio, video or artworks) will not be protected under copyright. For example a public speech delivered by someone will not be copyrighted unless it is recorded in written or recorded format.Copyright Infringement
If anyone uses a copyrighted work in way that exploits the rights of the original owner as provided by the copyright laws, it is called copyright infringement. The terms "theft" or "piracy" or "freebooting" is used to refer to copyright infringement. The violator of copyright may have to pay penalty as per the laws existing in the country.Piracy refers to unauthorized copying and distribution of copyrighted materials. It is common in the case of films, music and publishing industry. The term freebooting refers to the act of downloading someone else's copyright-protected material, often from YouTube, and uploading it into sites like FaceBook,Twitter and similar websites.
Fair Use
Fair use permits the usage of copyrighted material without the permission of its copyright owner. Fair use allows limited rights of copying the material for educational and research purposes. Also if you are writing a literary criticism, commentary or report, it is not violation of copyright.Indian Copyright Act 1957
The copyright in India is governed by Copyright Act 1957 which was amended in 2012. The first copyright legislation in India was the Indian Copyright Act, 1914.The following are protected under the Act:
- artistic work including a painting, a sculpture, a drawing (including a diagram, map, chart or plan), an engraving, a photograph, a work of architecture or artistic craftsmanship, dramatic work,
- literary work (including computer programmes, tables, compilations and computer databases),
- musical work (including music as well as graphical notation),
- sound recording, and
- cinematograph film
The duration of copyright protection in case of literarcy, dramatic and artistic works is the lifetime of the author + sixty years from the beginning of the calendar year next following the year in which the author dies. Other cases, it is sixty years from the beginning of the calendar years next following the year in which the work is first published.
The infringement of copyright is a cognizable offence punishable with for a term which shall not be less than six months but which may extend to three years with a fine which shall not be less than INR 50,000 but may extend to INR 2,00,000.
Trademark and Patent
A trademark, trade mark, or trade-mark is a recognizable sign, design, or expression which identifies products or services of a particular source from those of others, although trademarks used to identify services are usually called service marks. (Wikipedia).A trademark may be designated by the following symbols:
- ™ (the "trademark symbol", which is the letters "TM" in superscript, for an unregistered trademark, a mark used to promote or brand goods)
- ℠ (which is the letters "SM" in superscript, for an unregistered service mark, a mark used to promote or brand services)
- ® (the letter "R" surrounded by a circle, for a registered trademark)
A trademark registration may remain in force indefinitely, or expire without specific regard to its age.
Patent
A patent is a right granted to an inventor by the federal government that permits the inventor to exclude others from making, selling or using the invention for a period of time. The patent system is designed to encourage inventions that are unique and useful to society. In most countries the term of rights for patents is 20 years.Plagiarism
Plagiarism is to steal and pass the ideas of some else as your own ideas. Copying ideas or words from a work and using it without giving due credit to the rightful owner is plagiarism. Plagiarism can be avoided if you cite the sources of the original idea or content.Using poems, articles or other writing you found on the web without providing citation to the original creator is plagiarism. So whenever you take such material from the Internet do look for the copyright and usage policy.
Public Domain
Links to Public Domain Materials
- Internet Archive : A digital library of Internet sites and other cultural artifacts in digital form.
- Wikimedia Commons: freely usable media files to which anyone can contribute
- Library of Congress Digital Collections: World's largest library offering free digital content. Some may be copyrighted.
- Europeana Collections: Europe's digital platform for cultural heritage.
- The Commons Flickr: hidden treasures from the world's public photography archives
- Wikisource: the free library that anyone can improve
- Free ebooks - Project Gutenberg: offers over 54,000 free eBooks
- Open Images: an open media platform that offers online access to audiovisual archive material to stimulate creative reuse.
- Creative Commons: legally share your knowledge and creativity to build a more equitable, accessible, and innovative world
Further Reading
Monday, 11 November 2019
Digital Footprint
IP Address
- By using the ipconfig command in a command prompt
- By checking the Loal Area Connection properties (available under Network and Sharing Center)
Domain Names
Cookies
How to Manage Digital Footprints
Think before you post: Think before you post anything online. Online communications are instant and it may not be possible to remove them forever.
Sunday, 10 November 2019
Awareness Programme on Cyber Safety and Ethical Hacking
 |
| Mr. Sidharth talking about Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking |
 |
| ||||
|
| ||||
Saturday, 2 November 2019
Monday, 28 October 2019
Social Media and Social Networking
Social Media
Social media are the online tools and technologies that help us to create, share and exchange information in various formats via virtual communities and network. We make use of the social media for interaction, collaboration and content-sharing. Social media is a very broad term that includes different types of media like videos, wikis, blogs, pictures etc.Social media facilitate the development of online social networks. Social media plays an important role in enhancing education by making access to information quick and easy.Social Networking
Social networking aims to connect you with other people. It is a service that provides yo a platform to build social relations with other people. You do social networking on social media websites like facebook.Social Media Tools
Facebook is a popular free social networking website that allows registered users to create profiles, upload photos and video, send messages and keep in touch with friends, family and colleagues. Facebook was launched in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg. Facebook has more than 2.2 billion monthly active users as of January 2018. The issues on Facebook include internet privacy, fake information and shadow profiles. Statistics says Internet users within the United States spend more time on Facebook than any other website.Twitter founded in 2006, is a micro-blogging service which provides facility to broadcast short messages/posts. These posts are called tweets. Tweets were originally restricted to 140 characters, but on November 7, 2017, this limit was doubled for all languages except Japanese, Korean, and Chinese. The user can be tagged in a post by typing '@' before his username, also called 'handle'. The users can follow each other on Twitter. Individual tweets can be forwarded by other users to their own feed, a process known as a "retweet". Users can group posts together by topic or type by use of hashtags – words or phrases prefixed with a "#" sign.
Tuesday, 22 October 2019
Information Literary: Evaluating Internet Resources
The Internet has become the major source of information today. Information is easily available in different formats on the Internet. There is no doubt that the Internet is a boon for students and educators, but finding quality and authentic information from the Internet is a difficult task because of the sheer volume of information available. Unlike the traditional information sources like books, newspapers, magazines or television, information available on the Internet is not verified for accuracy or quality. Anyone can publish almost anything on the Internet and it may not be possible to verify the authenticity of the publisher or the information.
Though there are no standard set of rules available to assess the reliability and authenticity of Internet resources, the following criteria are suggested to ensure the authenticity of a web resource.
Authority
It is important to check the authority of the person or organisation who is responsible for the content your are accessing. If the information regarding the person or institution who have created the content is available, we may try to ascertain the authenticity of the information based on the reputation and credibility of the person or institution concerned. If no information is available about the creator of the information, then the information may be considered as unreliable.
In general, the following questions are to be answered to confirm authority of information
- Is the name of the author/creator provided?
- Are his/her credentials listed (occupation, years of experience, position or education)?
- What are the qualification and affiliations of the author?
- Are there contact information like a postal address, phone number or email id available?
- Is it a standalone page or a comment on a site?
- Is there any link to the organisation to which the author belong and is the information posted on the institutional website?
- Are there citations/references to other works?
- What about the domain name/URL of the web resource? Do they provide any clues regarding the authenticity of the web resource as mentioned below?
Sources like Wikis cannot be considered as authentic, as anyone can modify the information with reviewing.
Accuracy
Look whether the information is provided on on online magazine or journal or similar platforms. If the resource is an online magazine or journal the content will be accurate as they have a system of peer-review before accepting materials for publication.
An authentic resource will have its sources listed clearly so that the factual information provided can
be verified. Also check whether there are any spelling or grammatical errors in the resource. Any such errors shows lack of care and it also indicates that there is no quality control or proof reading done before publishing information
Objectivity
The objectivity of a resource is important in evaluating an Internet resources. Objectivity means the content of the resources is based on facts and not influenced by personal feelings or prejudices or bias of the author. Some authors may project their personal views as facts.
Currency
Consider the date of publication of the resource. See whether the information is up-to-date checking when the information was first published and when was it last updated. Depending on the nature of the information provided, the currency of information is very important.
Coverage
Coverage means the extend to which the topic is dealt with. Does the author cover the topic at hand comprehensively and cites accurate and current sources?
See the style of presentation of the content and the purpose of the site or resource. The information provided with a commercial purpose like selling a product may not be trustworthy.
Appearance
This concerns with the general look and feel of the web resource. See whether the site appears to be well organised with proper navigation and the links working or not. A well maintained site with proper links to resources cited for further reading will be more reliable that a badly presented web resource.
Remember, a web resource may not reliable just because it has presented the information in an attractive manner with charts and pictures.
Ask yourself these questions before using resources from the World Wide Web:
Author
Is the name of the author/creator on the page?
Are his/her credentials listed (occupation, years of experience, position or education)?
Is the author qualified to write on the given topic? Why?
Is there contact information, such as an email address, somewhere on the page?
Is there a link to a homepage?
If there is a link to a homepage, is it for an individual or for an organization?
If the author is with an organization, does it appear to support or sponsor the page?
What does the domain name/URL reveal about the source of the information, if anything?
If the owner is not identified, what can you tell about the origin of the site from the address?
Purpose
Knowing the motive behind the page's creation can help you judge its content.
Who is the intended audience?
Scholarly audience or experts?
General public or novices?
If not stated, what do you think is the purpose of the site? Is the purpose to:
Inform or Teach?
Explain or Enlighten?
Persuade?
Sell a Product?
Objectivity
Is the information covered fact, opinion, or propaganda?
Is the author's point-of-view objective and impartial?
Is the language free of emotion-rousing words and bias?
Is the author affiliated with an organization?
Does the author's affiliation with an institution or organization appear to bias the information?
Does the content of the page have the official approval of the institution, organization, or company?
Accuracy
Are the sources for factual information clearly listed so that the information can be verified?
Is it clear who has the ultimate responsibility for the accuracy of the content of the material?
Can you verify any of the information in independent sources or from your own knowledge?
Has the information been reviewed or refereed?
Is the information free of grammatical, spelling, or typographical errors?
Reliability and Credibility
Why should anyone believe information from this site?
Does the information appear to be valid and well-researched, or is it unsupported by evidence?
Are quotes and other strong assertions backed by sources that you could check through other means?
What institution (company, government, university, etc.) supports this information?
If it is an institution, have you heard of it before? Can you find more information about it?
Is there a non-Web equivalent of this material that would provide a way of verifying its legitimacy?
Currency
If timeliness of the information is important, is it kept up-to-date?
Is there an indication of when the site was last updated?
Links
Are links related to the topic and useful to the purpose of the site?
Are links still current, or have they become dead ends?
What kinds of sources are linked?
Are the links evaluated or annotated in any way?
Note: The quality of Web pages linked to the original Web page may vary; therefore, you must always evaluate each Web site independently.
Source for the above questions:
https://www.library.georgetown.edu/tutorials/research-guides/evaluating-internet-content
Social Media
The credibility of the information available on social media cannot be assessed as easily as on the Internet because the misinformation and rumours can be spread quickly on social media like Facebook, Twitter, WhatsApp etc.
The practice of using social media platforms like Facebook and WhatsApp to disseminate false information is bringing in a dangerous trend. There have been numerous instances of fake news misleading people, spreading false propaganda or maligning people as well as entire communities. Most of the users forward the information received without verifying the authenticity of information.
India now has the second highest number of internet users in the world after China. About 27% of Indian population are Internet users.
The criteria listed above can also be applied in verifying the reliability of information on social media.
When you get a email or a social media message you find doubtful, do a Google search and the truth can be found out.
Do not forward or spread any such messages without verifying its authenticity.
The following sites will be useful in verifying the email or social media hoaxes
http://hoax-slayer.com/
http://www.hoaxorfact.com/
If you have completed this lesson, please see the tasks given to assess a web resource finding answers to the questions listed above.
Information Literacy: How to Find Information
What is Information Literacy
Finding Information
Search Engines
Web Directories
Google Search Tips
Other Search Engines
Kiddle is a safe visual search engine for kids.
Multimedia Search
Desktop Search Tools
Monday, 21 October 2019
Internet basics
History of Internet
• 1960 – ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network)
• 1970’s – TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol
• 1990 – World Wide Web (WWW)
The complete history and origin of Internet
Internet V/s World Wide Web
• A network, in computing, is a group of devices that can communicate each other and share resources.
• Internet is a network of networks. It is a global network of billions of computers and many other electronic devices.
How the Internet Works?
IP Address
• Every computer connected to a network has its own unique number, called an IP address.
• IPv4 address is 32 bits (4 bytes) long and consists of two components: network component and host component.
• Each of the 4 bytes is represented by a number from 0 to 255, separated with dots.
• For example in 216.52.1.250.
• IPv6 creates more complex newer alphanumeric IP addresses such as 2400:cb00:2048:1::c629:d7a2.
TCP/IP
TCP/IP, or the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, is a suite of communication protocols used to interconnect network devices on the internet. TCP/IP can also be used as a communications protocol in a private computer network like an Intranet
Request and Response
In a typical WWW example, you type in a URL in your browser’s location window, and press enter.
Your browser then sends a message (request) to a web server, requesting for a given HTML page.
The web server sends back the page, or a response if the page cannot be found
Domain Name System
• The Domain Name System (DNS) assigns recognizable and easy to remember host names instead of IP address
• www.wikipedia.org - IP address 103.102.166.224
• The first-level set of domain names are the top-level domains (TLDs)
• Generic Domain - .com, .biz, .gov, .org
• Country Level Domain - .in, .uk, .us
• Below this are the second-level and third-level domain names. They appear directly left to TLDs
• The registration of the domain names is usually administered by domain name registrars
• Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) authorises domain name registrars
.IN Domains
• .IN is India's top-level domain on the Internet. Like .COM, .IN can be used for e-mail, Web sites, and other applications. But unlike other domains, .IN is a unique symbol of India and its role in the world.
• .IN domains are easy to buy, easy to use, fast and reliable! Anyone can register an .IN domain
• INRegistry is the official .IN registry. It was appointed by the government of India, and is operated under the authority of NIXI, the National Internet eXchange of India.
.NIC.IN, .EDU.IN & .GOV.IN
• The Domain name 'NIC.IN' is owned by National Informatics Centre (NIC) and the same can be allocated ONLY to Indian Government Entities
• NIC is the authorised registrar for 'GOV.IN' Domains and it is advised to all Government Departments (Central & State) to host their websites under 'GOV.IN' Domain names
• ERNET (Education and Research Network) is the exclusive registrar for the AC.IN, EDU.IN & RES.IN Domain names.
Web Browsers
• A web browser is a software application for accessing information on the World Wide Web.
• The first web browser, called WorldWideWeb, was created in 1990 by Sir Tim Berners-Lee
• Mosaic (1993) is credited as "the world's first popular browser“
• Popular browsers
• Google Chrome
• Apple Safari
• Opera
• Internet Explorer
• Mozilla Firefox
Websites
• A website is a collection of web pages and related content that is identified by a common domain name and published on at least one web server. (Wikipedia)
• It will have a homepage and many related pages/files
• Homepage refers to the main page that provides access to all the other pages or information on the site
• A Web Page is the basic unit of every website
• It may contain text and multimedia
Hyperlink
• A hyperlink or link is a word, phrase or image clicking on which you can get access to a resource on the Internet.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
• Uniform Resource Locator uniquely identifies a document over the internet.
• Domain name is component of URL
• We access a resource through the URL
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language)
Hypertext Markup Language is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. Developed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1990, HTML provides for the structure of a web page.
You can learn HTML through this tutorial
Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
An Internet service provider is an organisation that provides services for accessing, using, or participating in the Internet. As we know, Internet is a network of networks. We get connected to the Internet through the ISPs.
• ISP is a company like BSNL that offers its customer access to the Internet.
• ISP’s allot your computer an IP Address and provides access DNS server.
• ISPs in India:
• BSNL, MTNL
• Airtel
• Reliance Jio
• Idea
• Vodafone etc.
Who Controls the Internet?
• The Internet is a public, cooperative, and independent network. The following bodies controls some aspects of the Internet.
• Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN): Its task is to manage the logistics of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and domain names.
• World Wide Web Consortium (W3C): Its task is to develop and tests advanced Internet technologies.
Sunday, 13 October 2019
Saturday, 12 October 2019
Four Rules for Real-world Safety - NetSmartKidz
NetSmartzKids-KnowTheRules from NCMEC on Vimeo.
Check first; take a friend; tell people "NO"; tell a trusted adult; now you're ready to go! Watch Clicky rap his way into teaching you the 4 rules for real-world safety.
Information Literacy: Sources of Information
An information source is a person, thing, or place from which information comes, arises, or is obtained. The information source can be a person, an article, a website, a documentary, an organisation etc.. That source might then inform a person about something or provide knowledge about it.
- Documentary Sources - published or recorded documents of knowledge
- Non-documentary sources - are not recorded or published. Include the information received from interacting with researchers, colleagues, consultants and various other sources like organisations.
Documentary sources are divided into separate distinct categories, primary, secondary, and tertiary
Primary sources provide first hand and latest information on any topic. A subject becomes a discipline in its own right when independent primary sources begin to be produced in that area.
- Literary creation: novels, short stories, poems, etc.
- Artifacts (e.g. coins, plant specimens, fossils, furniture, tools, clothing, all from the time under study);
- Audio recordings (e.g. radio programs)
- Diaries;
- Internet communications on email, listservs;
- Interviews (e.g., oral histories, telephone, e-mail);
- Journal articles published in peer-reviewed publications;
- Letters;
- Newspaper articles written at the time;
- Original Documents (i.e. birth certificate, will, marriage license, trial transcript);
- Patents;
- Photographs
- Proceedings of Meetings, conferences and symposia;
- Records of organizations, government agencies (e.g. annual report, treaty, constitution, government document);
- Speeches;
- Survey Research (e.g., market surveys, public opinion polls);
- Video recordings (e.g. television programs);
- Works of art, architecture, literature, and music (e.g., paintings, sculptures, musical scores, buildings, novels, poems).
- Web site.
The secondary sources provide digested information and serve as a pointer to the primary source of information.
- Bibliographies (also considered tertiary);
- Biographical works;
- Commentaries, criticisms;
- Dictionaries, Encyclopedias (also considered tertiary);
- Histories;
- Literary criticism such as Journal articles;
- Magazine and newspaper articles;
- Monographs, other than fiction and autobiography;
- Textbooks (also considered tertiary);
- Web site (also considered primary).
- Almanacs;
- Bibliographies (also considered secondary);
- Chronologies;
- Dictionaries and Encyclopedias (also considered secondary);
- Directories;
- Fact books;
- Guidebooks;
- Indexes, abstracts, bibliographies used to locate primary and secondary sources;
- Manuals;
- Textbooks (also be secondary).
Friday, 11 October 2019
Let's be Cyber Smart - Welcome
Today we cannot think about a world without Internet, computers and smart phones. Internet is a valuable source for information and entertainment. Unfortunately, Internet has got its dangers also to offer. Malware, spams, online predators, identity thieves, false information, cyber bullying and other treats are waiting there online. If we are not careful, we may fall prey to these dangers which ahve have unforeseen consequences. Most of us are not aware of these cyber threats ro do not care much to keep ourselves safe online.
The project aims to make you aware of the cyber world better and to equip you to learn the tips and tricks to be safe online and be responsible netizens. The project will make you familiarise with various cyber safety issues and how to safeguard against them. You will in turn be able to guide other students on how to be safe online.
At the end of the project, we aim to select some "Cyber Ambassadors" for our school who will spread awareness among the students on cyber safety measures.
What will you learn?
Basic for Internet
Cyber Threats and How to be Safe Online
Phase I: Introduction to Cyber Security and Internet Safety
Phase II: Expert Talks and Interaction
Phase III : Spreading Awareness
Phase IV: Final Assessment and Selection of Cyber Ambassadors